Edge vs. Cloud: Choosing the Right IoT Computing Strategy
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming industries by enabling real-time data collection, automation, and advanced analytics. However, one of the biggest challenges in IoT deployment is deciding where to process data—on the **edge** or in the **cloud**. Both computing strategies have distinct advantages and trade-offs, and choosing the right approach depends on factors like latency, bandwidth, security, and cost.
Understanding Edge and Cloud Computing in IoT
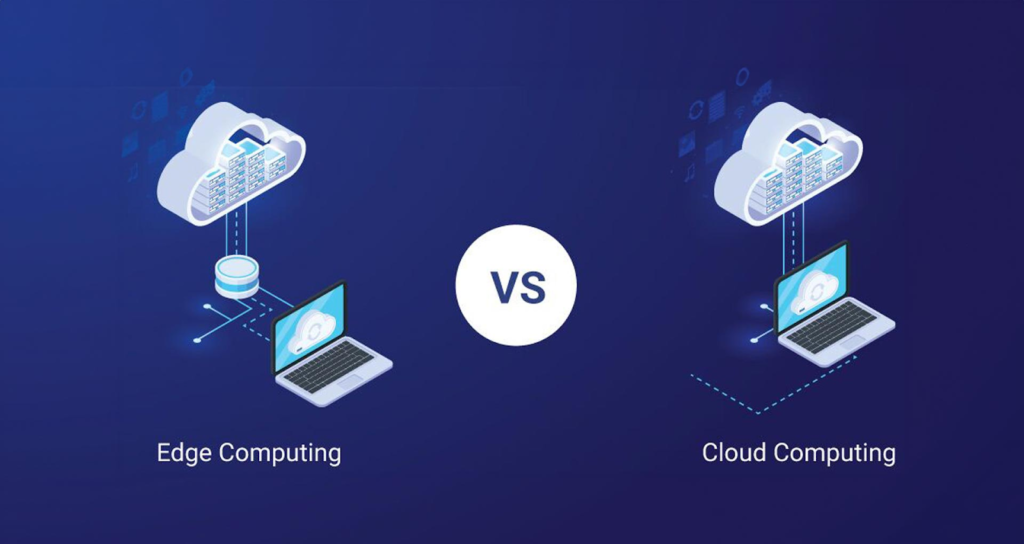
1. Edge Computing: Processing Data at the Source
Edge computing involves processing data locally, near the IoT devices, rather than sending it to a centralized cloud server. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage while improving real-time decision-making.
Key Benefits:
– Low Latency: Critical for applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring.
– Bandwidth Efficiency: Reduces the need to transmit large volumes of raw data to the cloud.
– Enhanced Privacy & Security: Sensitive data can be processed locally, minimizing exposure to cyber threats.
– Offline Operation: Edge devices can function even without an internet connection.
Use Cases:
– Smart factories (predictive maintenance, machine vision)
– Autonomous drones and vehicles
– Real-time surveillance and facial recognition
2. Cloud Computing: Centralized Data Processing
Cloud computing relies on remote servers to store and process IoT data, offering virtually unlimited storage and computational power.
Key Benefits:
– Scalability: Easily handles massive datasets and complex analytics.
– Advanced AI & Machine Learning: Cloud platforms support large-scale data modeling.
– Cost-Effective Storage: Long-term data retention is more economical than local storage.
– Global Accessibility: Data can be accessed and managed from anywhere.
Use Cases:
– Smart city infrastructure (traffic management, energy optimization)
– Enterprise IoT analytics (customer behavior, supply chain tracking)
– Healthcare data aggregation (patient records, predictive diagnostics)
Hybrid Approach: The Best of Both Worlds
Many organizations adopt a hybrid IoT strategy, combining edge and cloud computing:
– Edge handles real-time processing and immediate actions.
– Cloud managed long-term storage, big data analytics, and AI model training.
For example, a smart security camera might use edge computing to detect intruders in real-time while sending video footage to the cloud for forensic analysis.
Conclusion: Which One Should You Choose?
The decision between edge and cloud computing depends on your IoT application’s requirements:
– Choose Edge if low latency, offline capability, or data privacy is critical.
– Choose Cloud if you need massive scalability, deep learning, or centralized data management.
– Hybrid Solutions are ideal for balancing speed, efficiency, and scalability.
By carefully evaluating your needs, you can optimize your IoT infrastructure for performance, cost, and security.